Am I Neurodivergent? A Guide to Self-Assessment and Understanding
January 9, 2025 | By Morgan Hayes
What Does It Mean to Be Neurodivergent?
The term neurodivergent describes individuals whose brains work differently from the typical neurological framework, often referred to as "neurotypical." These differences influence how a person processes information, interacts with the world, and experiences emotions. Neurodivergence encompasses a broad spectrum of conditions, including autism, ADHD, dyslexia, and more, which are not deficits but variations in human cognition and behavior.
Why is understanding neurodivergence important?
Recognizing and embracing neurodivergence fosters self-awareness and reduces stigma, encouraging individuals to appreciate their unique strengths while acknowledging challenges. This awareness can help neurodivergent individuals access tools and strategies to navigate daily life successfully, enhancing their mental well-being and personal growth.
How Do You Test If You Are Neurodivergent?
Exploring Neurodivergent Tests
Determining whether you are neurodivergent often begins with a self-assessment or standardized screening test. These tests evaluate cognitive patterns, emotional responses, sensory sensitivities, and other factors commonly associated with neurodivergence. While our online neurodivergent test tool can provide insights, it is not a substitute for professional evaluation.

What to Expect in a Neurodivergent Test
A comprehensive neurodivergent assessment typically involves:
- Interviews: A psychologist may ask about your developmental history, behaviors, and challenges.
- Standardized Tests: These might measure memory, attention, language skills, and social understanding.
- Observations: Professionals often analyze how you respond to specific tasks or stimuli in controlled environments.
For those seeking clarity, using a structured test tailored to assess neurodivergent traits is an excellent first step. Take our free neurodivergent self-assessment tool to gain insights into your cognitive and emotional patterns, and let it guide you toward professional consultation and self-understanding.
What Are the 11 Types of Neurodivergence?
Neurodivergence spans a wide range of conditions that affect brain functioning and behavior. Studies, including those published by leading psychological research institutions, estimate that around 30% of the population exhibits neurodivergent traits. Here’s an overview of the most commonly recognized types:
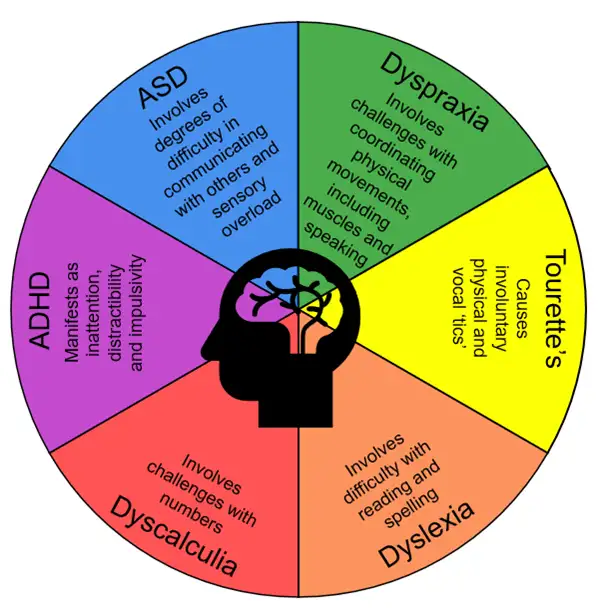
- Autism Spectrum Disorder (ASD): Characterized by differences in communication, behavior, and sensory processing.
- Attention-Deficit/Hyperactivity Disorder (ADHD): Involves challenges with attention, impulsivity, and hyperactivity.
- Dyslexia: Affects reading and language processing skills.
- Dyscalculia: Impacts mathematical abilities and number comprehension.
- Dysgraphia: Causes difficulties with writing, including handwriting and spelling.
- Dyspraxia: Involves challenges with motor coordination and planning.
- Sensory Processing Disorders: Lead to heightened or reduced sensitivity to sensory inputs.
- Tourette Syndrome: Characterized by involuntary tics and vocalizations.
- Intellectual Disabilities: Include a range of cognitive impairments affecting learning and problem-solving.
- Obsessive-Compulsive Disorder (OCD): Features intrusive thoughts and repetitive behaviors.
- Social Anxiety Disorders: Often linked to challenges in social settings, which may overlap with neurodivergent traits.
Each of these conditions represents unique ways the brain functions. While some individuals experience one type of neurodivergence, others may have co-occurring conditions, which further diversify their experiences.
Signs You Might Be Neurodivergent
Identifying neurodivergence often starts with recognizing behavioral or emotional patterns. Key signs include:
- Sensory Sensitivities: Unusual reactions to sensory inputs like noise, light, or textures, often leading to discomfort or overwhelm.
- Social Interaction Challenges: Difficulty interpreting social cues or building relationships, sometimes resulting in feelings of isolation.
- Focused Interests: Deep passion for specific topics or hobbies, pursued with exceptional intensity.
- Difficulty with Change: A strong preference for routines and discomfort with unexpected disruptions.
- Emotional Regulation Issues: Intense emotional responses or difficulty managing feelings effectively.
- Repetitive Behaviors: Actions like rocking or tapping, often used for self-soothing.
- Executive Functioning Challenges: Trouble with planning, organization, or managing time effectively.
While these traits don’t confirm neurodivergence, they can signal a need for further exploration. A neurodivergent self-assessment or consultation with a mental health professional can provide clarity.
Am I Neurodivergent or Just Different?
Differentiating Between Typical Behaviors and Neurodivergent Traits
It’s natural for everyone to exhibit unique behaviors, preferences, and thought patterns, but what distinguishes neurodivergence from general individuality? Neurodivergent traits are typically more consistent and noticeable, often affecting cognitive processes, social interactions, and sensory perceptions in ways that go beyond the norm. These traits may present challenges in environments designed for neurotypical individuals, such as schools or workplaces, while simultaneously offering unique strengths, like creative problem-solving or intense focus on specialized interests.
Occasionally struggling with social cues or focus is normal, but persistent difficulties in these areas may indicate neurodivergence.
The Importance of Professional Diagnosis vs. Self-Identification
A professional diagnosis provides a clinical understanding of neurodivergence, often including insights into strengths and coping strategies. It can also help individuals access accommodations or treatments tailored to their needs. However, self-identification plays an important role, especially for those who resonate with neurodivergent experiences but lack access to formal assessments.
Self-identification allows individuals to explore resources, join supportive communities, and begin understanding themselves better. For many, this journey starts with self-assessment tools, which, while not diagnostic, offer valuable direction and validation for seeking professional guidance.
What Qualifies You as Neurodivergent?
Criteria and Assessments Used by Professionals
Professionals assess neurodivergence through a combination of methods, including:

- Developmental History: Understanding early behaviors and milestones.
- Behavioral Observation: Examining current patterns and responses in various situations.
- Standardized Tests: Measuring cognitive functions, memory, and problem-solving abilities.
Such assessments aim to identify specific conditions like ADHD, autism, dyslexia, or sensory processing disorders. These diagnoses provide clarity and open doors to tailored interventions and accommodations.
The Role of Self-Assessment Tools
Self-assessment tools offer an accessible starting point for exploring neurodivergence. These tools typically include questionnaires focusing on behavioral, sensory, and cognitive traits. While not diagnostic, they can provide insights that encourage individuals to seek professional evaluations or self-reflect on their unique experiences.
Exploring High-Functioning Neurodivergence
What Does It Mean to Be High-Functioning?
The term "high-functioning" is often used to describe neurodivergent individuals who can perform daily tasks independently and exhibit skills that align with societal expectations. However, this term is frequently criticized within neurodivergent communities for oversimplifying the challenges faced by these individuals, as it often fails to account for invisible difficulties like burnout or sensory overload. Alternatives like "support needs" or "strength-based profiles" provide a more inclusive and accurate representation.However, it’s important to note that the term can be misleading, as it downplays underlying struggles or overlooks the need for support. For example, a high-functioning individual with autism might excel in academics but face significant challenges in social interactions or managing sensory overload.

Debunking Myths and Understanding the Challenges
- Myth: High-functioning individuals don’t face significant difficulties. Reality: Many high-functioning neurodivergent people encounter invisible challenges, including anxiety, burnout, or sensory sensitivities.
- Myth: High-functioning means less neurodivergent. Reality: Neurodivergence is not a spectrum of severity but of variation. Each individual has unique strengths and struggles, regardless of how they are labeled.
Understanding high-functioning neurodivergence requires moving beyond labels to focus on individual experiences, fostering empathy, and providing appropriate support tailored to specific needs.
Is Anxiety Considered Neurodivergent?
Exploring the Relationship Between Anxiety and Neurodivergence
Anxiety, a common mental health condition, is not inherently considered neurodivergent. However, the relationship between anxiety and neurodivergence is complex. Many neurodivergent individuals, such as those with autism or ADHD, experience co-occurring anxiety. This overlap is often due to heightened sensory processing, social challenges, or differences in executive functioning, which can contribute to anxious feelings.
Some people with chronic anxiety choose to self-identify as neurodivergent because it validates their lived experiences of feeling different from societal norms. While the term neurodivergent has traditionally referred to conditions like autism and ADHD, its evolving usage increasingly includes mental health challenges that significantly affect daily functioning.
Distinguishing Anxiety Disorders From Neurodivergent Conditions
Neurodivergent conditions are often developmental, present from an early age, and affect neurological functioning. Examples include autism, ADHD, and dyslexia. In contrast, anxiety disorders, such as generalized anxiety disorder (GAD) or panic disorder, can emerge at any stage of life and are not typically categorized as neurodivergent.
The distinction lies in the onset and nature of these conditions. Neurodivergence reflects a lifelong pattern of neurological differences, while anxiety disorders may result from environmental, genetic, or situational factors and can often be managed with therapy or medication.
Can You Self-Identify as Neurodivergent?
The Role of Self-Diagnosis in the Neurodivergent Community
Self-diagnosis is an important and valid starting point for many exploring their potential neurodivergence. Factors such as limited access to healthcare, stigma, or a lack of awareness about neurodivergent traits can delay or prevent formal diagnoses. Self-identifying allows individuals to research, seek support, and join communities that affirm their experiences.
For example, many adults with undiagnosed autism or ADHD discover their neurodivergence through self-reflection, online tools, or connecting with others who share similar traits. This process can be empowering, providing clarity and validation.
When to Seek Professional Help
While self-identification can be valuable, a professional diagnosis offers critical benefits, such as access to formal accommodations, therapies, or medications. It also provides a structured understanding of your traits and challenges. Seeking professional help is especially important if neurodivergent traits significantly impact daily life, relationships, or work.
Professionals trained in neurodiversity-informed care can offer compassionate evaluations, helping individuals gain insights while respecting their lived experiences.
What Do Neurodivergent People Struggle With?
Strategies for Coping and Thriving
- Self-Awareness: Understanding personal triggers and strengths to navigate challenges effectively.
- Routine Building: Establishing consistent routines to reduce stress and increase productivity.
- Accommodations: Using tools like noise-canceling headphones, time-management apps, or sensory-friendly environments.
- Community Support: Joining neurodivergent communities to share experiences and resources.
- Professional Help: Seeking therapy, coaching, or mentorship tailored to neurodivergent individuals.
Recognizing both the challenges and unique strengths of neurodivergent individuals fosters resilience and enables them to thrive in diverse settings. By embracing tailored strategies and supportive networks, neurodivergent individuals can lead fulfilling, empowered lives.
How to Get a Neurodivergent Assessment?
Steps to Finding a Reliable Neurodivergent Assessment
- Research Qualified Professionals: Look for licensed psychologists, neuropsychologists, or psychiatrists with experience in neurodiversity and related conditions such as ADHD, autism, or learning disorders.
- Seek Recommendations: Ask for referrals from trusted sources, such as primary care providers, community support groups, or online forums dedicated to neurodiversity.
- Verify Credentials: Ensure the professional has expertise in administering comprehensive assessments for neurodivergence.
- Consider Accessibility: Look into options like online evaluations or clinics that specialize in neurodiversity, especially if local resources are limited.
- Prepare for the Process: Gather relevant documents, including developmental history, academic records, or previous evaluations, to share with the assessor.
What to Expect From the Evaluation Process
- Initial Consultation: The process often begins with a discussion about your concerns, history, and goals for the assessment.
- Standardized Testing: You may undergo cognitive, behavioral, or sensory assessments to evaluate traits associated with neurodivergence.
- Observation: Some professionals may observe how you interact in specific situations or respond to certain tasks.
- Feedback and Diagnosis: The evaluator provides a detailed report summarizing findings, which may include a diagnosis, strengths, challenges, and recommendations for support or accommodations.
The outcome of a neurodivergent assessment can offer valuable insights and help individuals access resources to better navigate their unique needs.
Frequently Asked Questions
How do I know if I’m neurodivergent? If you consistently experience traits such as sensory sensitivities, difficulties with executive functioning, or social challenges that align with neurodivergent conditions, you might be neurodivergent. Try our free self-assessment tool for initial insights into your unique traits.
Is toe walking a sign of neurodivergence?
Toe walking is often associated with neurodivergent conditions like autism or sensory processing disorders, but it is not exclusive to them. It can also occur due to physical conditions, so a professional evaluation is essential for an accurate understanding.
What not to say to a neurodivergent person?
Avoid dismissive phrases like “You don’t seem neurodivergent,” or “Everyone feels that way sometimes.” Such comments invalidate their experiences. Instead, focus on listening and understanding their perspective.
Can I be neurodivergent and not autistic?
Yes, neurodivergence encompasses a range of conditions beyond autism, including ADHD, dyslexia, dyspraxia, and more. Many individuals identify as neurodivergent without an autism diagnosis.
What are the hidden strengths of neurodiverse people?
Neurodiverse individuals often excel in areas such as pattern recognition, creativity, problem-solving, and innovation. Their unique perspectives and abilities can lead to exceptional contributions in fields like technology, art, and science.
Taking the Next Steps in Understanding Your Neurodivergence
Understanding your neurodivergence is a journey of self-awareness, acceptance, and empowerment. Whether you seek a professional diagnosis or rely on self-identification, recognizing your unique traits is the first step toward personal growth.
Encouragement to Use Available Resources:
Discover how our free neurodivergent test can help you identify your unique traits and connect with like-minded communities. Take the test now.
The Importance of Professional Guidance:
When possible, consult with specialists to gain a clearer picture of your neurodivergent traits. Professional assessments can help unlock access to accommodations, therapies, and strategies that enhance your quality of life.