क्या मैं न्यूरोडाइवर्जेंट हूँ? ADHD, आलस और कार्यकारी शिथिलता को समझने के लिए हमारा टेस्ट
July 6, 2025 | By Morgan Hayes
क्या आप कभी सोचते हैं कि आप आलसी हैं, या आपके ध्यान और प्रेरणा संबंधी संघर्षों के पीछे कुछ और है? कई न्यूरोडाइवर्जेंट व्यक्ति, विशेष रूप से ADHD वाले, इन भावनाओं से जूझते हैं, और अक्सर खुद को उन चीज़ों के लिए दोषी ठहराते हैं जो वास्तव में अद्वितीय न्यूरोलॉजिकल अंतर हैं। यदि आपने पूछा है, 'क्या मैं न्यूरोडाइवर्जेंट हूँ, या सिर्फ अजीब, आलसी, या चिंतित हूँ?', तो यह लेख आपके लिए है। हम कार्यकारी शिथिलता के लक्षणों और न्यूरोडाइवर्जेंट मस्तिष्क द्वारा प्रेरणा को संभालने के अद्वितीय तरीकों में गहराई से उतरेंगे, जो आपको वह स्पष्टता और मान्यता प्रदान करेगा जिसके आप हकदार हैं। क्या आप अपनी अनूठी न्यूरोलॉजिकल प्रोफाइल का पता लगाने के लिए तैयार हैं? आज ही हमारे मुफ़्त न्यूरोडाइवर्जेंट टेस्ट के साथ आत्म-खोज की अपनी यात्रा शुरू करें।
आप आलसी क्यों नहीं हैं: "आलसी या ADHD" मिथक को समझना
"आलसी" होने का विचार अक्सर प्रयास या इच्छाशक्ति की कथित कमी से जुड़ा होता है। हालाँकि, कई न्यूरोडाइवर्जेंट व्यक्तियों के लिए, शुरुआत करने, ध्यान केंद्रित करने और पूरा करने में संघर्ष उनकी मस्तिष्क की वायरिंग से उत्पन्न होता है, न कि किसी नैतिक विफलता से। यह इस आम ग़लतफ़हमी को नए सिरे से देखने का समय है।
न्यूरोडाइवर्जेंट जीवन में "आलस" का कलंक
बचपन से ही, कई ऐसे लोगों को जिन्हें बाद में न्यूरोडाइवर्जेंट के रूप में पहचाना जाता है, उन्हें "आलसी," "प्रेरणाहीन," या "पर्याप्त प्रयास नहीं कर रहे हैं" के रूप में लेबल किया जाता है। "आलस" का यह कलंक गहरा आत्म-दोष और शर्म पैदा कर सकता है। कल्पना कीजिए कि आप वास्तव में किसी कार्य को पूरा करना चाहते हैं, लेकिन आपको शुरू करने से रोकने वाली एक अदृश्य दीवार का अनुभव होता है। यह आलस नहीं है; यह एक वास्तविक आंतरिक बाधा है जिसे पारंपरिक प्रेरक तकनीकें अक्सर संबोधित करने में विफल रहती हैं। इस अंतर को समझना आत्म-स्वीकृति की ओर पहला कदम है।

परिप्रेक्ष्य बदलना: नैतिक विफलता से न्यूरोलॉजिकल अंतर तक
चुनौतियों को व्यक्तिगत कमियों के रूप में देखने के बजाय, हम अपने परिप्रेक्ष्य को न्यूरोलॉजिकल अंतरों की ओर स्थानांतरित कर सकते हैं। एक न्यूरोडाइवर्जेंट मस्तिष्क जानकारी को संसाधित करता है, ध्यान को नियंत्रित करता है, और अद्वितीय तरीकों से कार्यों का प्रबंधन करता है। जो बाहर से "आलस" जैसा दिखता है वह वास्तव में कार्यकारी शिथिलता का एक प्रकटीकरण हो सकता है, यह मस्तिष्क की "प्रबंधन प्रणाली" से जुड़ी कठिनाइयों का वर्णन करता है। इस बदलाव को अपनाना आपको स्वयं की अधिक सटीक और दयालु समझ प्राप्त करने में मदद कर सकता है।
कार्यकारी शिथिलता के लक्षण समझाए गए
तो, कार्यकारी शिथिलता वास्तव में क्या है? यह अपने आप में कोई निदान नहीं है, बल्कि मस्तिष्क के कार्यकारी कार्यों से संबंधित चुनौतियों का एक समूह है। ये उच्च-स्तरीय संज्ञानात्मक कौशल हैं जो अन्य क्षमताओं और व्यवहारों को नियंत्रित और समन्वयित करते हैं। जब ये कार्य सामान्य रूप से काम नहीं करते हैं, तो दैनिक कार्य अत्यधिक कठिन महसूस हो सकते हैं।
प्रभावित मुख्य क्षेत्र: योजना बनाना, ध्यान केंद्रित करना और कार्य शुरू करना
कार्यकारी शिथिलता के लक्षण कई मुख्य क्षेत्रों में प्रकट हो सकते हैं, जिससे रोजमर्रा का जीवन एक महत्वपूर्ण बाधा बन जाता है। इनमें योजना बनाने (लक्ष्य प्राप्त करने के लिए चरणों को व्यवस्थित करना), ध्यान केंद्रित करने (किसी कार्य पर ध्यान बनाए रखना), और कार्य शुरू करने (कुछ शुरू करना) में कठिनाइयाँ शामिल हैं। एक विस्तृत योजना वाली दिनचर्या की कल्पना करें, फिर भी उसे शुरू करने के लिए अत्यधिक मानसिक प्रयास की आवश्यकता होती है। यह इस बारे में नहीं है कि आप इसे नहीं करना चाहते हैं; बल्कि यह किसी विशिष्ट मस्तिष्क कार्य के उम्मीद के मुताबिक काम न करने के बारे में है। ये चुनौतियाँ अक्सर उन चीज़ों के केंद्र में होती हैं जिन्हें कई लोग प्रेरणा के साथ संघर्ष के रूप में अनुभव करते हैं।

कार्यकारी कार्य केवल "न चाहने" से कैसे भिन्न होता है
यह समझना महत्वपूर्ण है कि कार्यकारी कार्य में बाधा या केवल "कुछ न चाहने" में क्या अंतर है। "न चाहना" पसंद के आधार पर एक चुनाव का संकेत देता है। कार्यकारी शिथिलता, हालांकि, क्षमता की कमी का वर्णन करती है। यह एक ऐसी कार की तरह है जिसका इंजन पूरी टंकी गैस और एक उत्सुक ड्राइवर के बावजूद ठीक से काम नहीं करता है। इच्छा मौजूद है, लेकिन निष्पादन का तंत्र बाधित है। यह अंतर आपके स्वयं के अनुभवों को समझने के लिए एक दयालु लेंस प्रदान करता है।
ADHD और प्रेरणा: एक अद्वितीय संबंध
ADHD (ध्यान-अभाव/अतिसक्रियता विकार) न्यूरोडाइवर्जेंस के सबसे आम रूप से मान्यता प्राप्त रूपों में से एक है जहाँ प्रेरणा अद्वितीय रूप से काम करती है। ऐसा नहीं है कि ADHD वाले व्यक्तियों में प्रेरणा की कमी होती है; बल्कि, उनकी प्रेरक प्रणाली "न्यूरोटिपिकल" माने जाने वाले लोगों से भिन्न होती है। इससे उनकी क्षमताओं और प्रयासों के बारे में गलतफहमी हो सकती है।
डोपामाइन और रुचि-आधारित प्रेरणा की भूमिका
ADHD और प्रेरणा के मूल में न्यूरोट्रांसमीटर डोपामाइन है। डोपामाइन मस्तिष्क की पुरस्कार प्रणाली में एक महत्वपूर्ण भूमिका निभाता है, जो प्रेरणा, आनंद और ध्यान को प्रभावित करता है। ADHD मस्तिष्क में, डोपामाइन विनियमन असामान्य हो सकता है, जिससे किसी कार्य में शामिल होने के लिए उच्च उत्तेजना या रुचि की आवश्यकता होती है। यह रुचि-आधारित प्रेरणा की व्याख्या करता है: वे कार्य जो वास्तव में रोमांचक या नए हैं, वे तीव्र ध्यान केंद्रित कर सकते हैं, जबकि सामान्य या दीर्घकालिक कार्य शुरू करना या बनाए रखना अविश्वसनीय रूप से कठिन होते हैं। यह इच्छाशक्ति के बारे में नहीं है; यह मस्तिष्क रसायन विज्ञान के बारे में है।
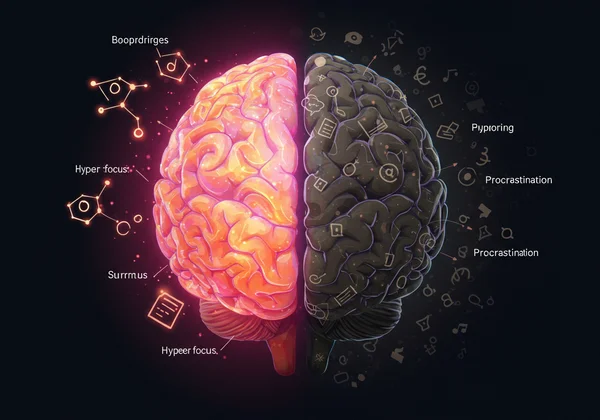
अति-केंद्रण बनाम टालमटोल: एक ही सिक्के के दो पहलू
यह अद्वितीय प्रेरक प्रोफ़ाइल अति-केंद्रण बनाम टालमटोल जैसे विरोधाभासों को जन्म दे सकती है। अति-केंद्रण किसी ऐसे कार्य पर तीव्र, निरंतर एकाग्रता है जो आकर्षक या पुरस्कृत करने वाला हो, अक्सर बाकी सब कुछ छोड़कर। यह रचनात्मक या बहुत दिलचस्प काम के लिए एक महाशक्ति हो सकती है। इसके विपरीत, टालमटोल अक्सर उन कार्यों के साथ होता है जिनमें तत्काल उत्तेजना या आंतरिक रुचि की कमी होती है, जिससे महत्वपूर्ण देरी और तनाव होता है। दोनों न्यूरोडाइवर्जेंट लक्षण प्रश्नोत्तरी सिक्के के दो पहलू हैं, जो ADHD मस्तिष्क के अपने कथित रुचि और पुरस्कार के आधार पर कार्यों को प्राथमिकता देने और संलग्न करने के अद्वितीय तरीके को दर्शाते हैं।
"क्या मैं न्यूरोडाइवर्जेंट हूँ या सिर्फ अजीब/चिंतित/भिन्न?"
कई व्यक्ति सोचते हैं, "क्या मैं न्यूरोडाइवर्जेंट हूँ या सिर्फ अजीब/चिंतित/भिन्न?" यह प्रश्न गहराई से महसूस किए गए आंतरिक अनुभवों को वर्गीकृत करने के एक सामान्य संघर्ष को दर्शाता है। अच्छी खबर यह है कि आप शायद "अजीब" नहीं हैं। आप उन लक्षणों का अनुभव कर रहे होंगे जो मानव न्यूरोलॉजिकल विविधता के एक व्यापक और जीवंत स्पेक्ट्रम के साथ संरेखित होते हैं। इस परिप्रेक्ष्य को अपनाने से अविश्वसनीय रूप से मुक्ति मिल सकती है।
न्यूरोडाइवर्जेंस का व्यापक स्पेक्ट्रम
न्यूरोडाइवर्जेंस एक प्रतिमान है जो न्यूरोलॉजिकल भिन्नताओं को प्राकृतिक और मूल्यवान मानवीय भिन्नताओं के रूप में देखता है। इसमें ADHD, ऑटिज़्म (ऑटिस्टिक व्यक्ति), डिस्लेक्सिया, डिसप्रैक्सिया, टॉरेट सिंड्रोम, और कई अन्य शामिल हैं, लेकिन यह इन्हीं तक सीमित नहीं है। न्यूरोडाइवर्जेंस के व्यापक स्पेक्ट्रम को समझने से व्यक्तियों को अपनी अनूठी संज्ञानात्मक प्रोफाइल को उन विकारों के रूप में नहीं, बल्कि दुनिया को देखने और बातचीत करने के अलग-अलग तरीकों के रूप में देखने में मदद मिलती है। यह समावेशी परिप्रेक्ष्य हमारी विविधताओं का जश्न मनाता है और स्वीकार करता है कि एक "विशिष्ट" मस्तिष्क होने के कई तरीकों में से सिर्फ एक है।
मान्यता और आत्म-स्वीकृति खोजना
कई लोगों के लिए, न्यूरोडाइवर्जेंस की अवधारणा की खोज से अपार राहत और अपनेपन की भावना आती है। यह उन जीवन भर के संघर्षों के लिए मान्यता और आत्म-स्वीकृति खोजने में मदद करता है जिन्हें पहले व्यक्तिगत विफलता का परिणाम माना जाता था। यह महसूस करना कि आपका मस्तिष्क अलग तरह से काम करता है, न कि दोषपूर्ण रूप से, सकारात्मक बदलाव के लिए एक शक्तिशाली उत्प्रेरक हो सकता है। यह ध्यान 'मुझमें क्या कमी है?' से बदलकर 'मैं अपने अनूठे मस्तिष्क का सबसे अच्छा समर्थन कैसे कर सकता हूँ?' की ओर ले जाता है। आत्म-समझ की यह यात्रा सशक्त है।

आत्म-दोष से परे जाना: समझ की ओर आपका मार्ग
आत्म-दोष से परे जाना आपके प्रामाणिक स्व को अपनाने की दिशा में एक महत्वपूर्ण कदम है। "आलसी या ADHD" प्रश्न न्यूरोलॉजिकल अंतरों की एक आम सामाजिक गलतफहमी को दर्शाता है। कार्यकारी शिथिलता और ADHD और प्रेरणा के अनूठे तरीके जैसे अवधारणाओं को समझकर, आप वर्षों की आंतरिक आलोचना को दूर करना शुरू कर सकते हैं। आपका मस्तिष्क टूटा हुआ नहीं है; यह बस एक विशिष्ट, अक्सर शानदार, तरीके से संरचित है।
यदि यह लेख आपके साथ प्रतिध्वनित हुआ है, और आप अपनी न्यूरोलॉजिकल प्रोफाइल को और अधिक जानने के लिए उत्सुक हैं, तो हम आपको आत्म-समझ की दिशा में एक महत्वपूर्ण कदम उठाने के लिए आमंत्रित करते हैं। हमारा मुफ़्त, उपयोग में आसान न्यूरोडाइवर्जेंट टेस्ट आपकी संभावित न्यूरोडाइवर्जेंट लक्षणों की पहचान करने में मदद करने के लिए एक प्रारंभिक स्क्रीनिंग प्रदान करता है। इसे एक सहायक शुरुआती बिंदु के रूप में डिज़ाइन किया गया है, न कि नैदानिक उपकरण के रूप में, जो आपकी यात्रा को सशक्त बनाने वाली अंतर्दृष्टि प्रदान करता है। आज ही हमारे न्यूरोडाइवर्जेंट लक्षणों की प्रश्नोत्तरी लेकर अपने बारे में अधिक जानें और न्यूरोडाइवर्जेंट समुदाय के भीतर अपनेपन की भावना खोजें।
न्यूरोडाइवर्जेंट लक्षण और प्रेरणा के बारे में अक्सर पूछे जाने वाले प्रश्न
न्यूरोडाइवर्जेंट होने के संकेत क्या हैं?
न्यूरोडाइवर्जेंट होने के संकेत क्या हैं? सामान्य संकेत विशिष्ट न्यूरोटाइप के आधार पर व्यापक रूप से भिन्न हो सकते हैं, लेकिन अक्सर सामाजिक संचार, संवेदी प्रसंस्करण, ध्यान विनियमन, कार्यकारी कार्यों (जैसे योजना और संगठन), और सीखने की शैलियों में अंतर शामिल होते हैं। ये आवश्यक रूप से कमियाँ नहीं हैं, बल्कि दुनिया का अनुभव करने के विशिष्ट तरीके हैं। हमारा न्यूरोडाइवर्जेंट स्क्रीनिंग टूल इन क्षेत्रों में प्रारंभिक अंतर्दृष्टि प्रदान कर सकता है।
क्या आप न्यूरोडाइवर्जेंट हो सकते हैं और ADHD या ऑटिज़्म नहीं हो सकता है?
हाँ, बिल्कुल। क्या आप न्यूरोडाइवर्जेंट हो सकते हैं और ADHD या ऑटिज़्म नहीं हो सकता है? न्यूरोडाइवर्जेंस शब्द व्यापक है, जिसमें ADHD और ऑटिज़्म से परे कई न्यूरोलॉजिकल अंतर शामिल हैं। इसमें डिस्लेक्सिया, डिसप्रैक्सिया, टॉरेट सिंड्रोम, डिसकैलकुलिया, और बहुत कुछ शामिल हैं। प्रत्येक न्यूरोटाइप अद्वितीय संज्ञानात्मक चुनौतियों और शक्तियों का एक सेट प्रस्तुत करता है। हमारी साइट एक व्यापक न्यूरोडाइवर्जेंट टेस्ट प्रदान करती है जो विभिन्न पहलुओं पर प्रकाश डालता है।
न्यूरोडाइवर्जेंस का परीक्षण कैसे किया जाता है?
न्यूरोडाइवर्जेंस का परीक्षण कैसे किया जाता है? जबकि हमारे न्यूरोडाइवर्जेंट टेस्ट जैसे ऑनलाइन स्क्रीनिंग टूल मूल्यवान प्रारंभिक अंतर्दृष्टि प्रदान कर सकते हैं, एक औपचारिक निदान के लिए एक योग्य पेशेवर द्वारा व्यापक मूल्यांकन की आवश्यकता होती है। इसमें एक मनोवैज्ञानिक, मनोचिकित्सक, या न्यूरोलॉजिस्ट शामिल हो सकते हैं, जो साक्षात्कार, अवलोकन और मानकीकृत परीक्षण करेंगे। हमारा मुफ़्त ऑनलाइन टूल आपको स्वयं को बेहतर ढंग से समझने और यह तय करने में मदद करने के लिए एक उत्कृष्ट पहला कदम है कि क्या आप पेशेवर मूल्यांकन कराना चाहते हैं। हमारे मुफ़्त न्यूरोडाइवर्जेंट टेस्ट के साथ अपनी यात्रा शुरू करें।
न्यूरोडाइवर्जेंट मस्तिष्क की ताकतें क्या हैं?
न्यूरोडाइवर्जेंट मस्तिष्क की ताकतें क्या हैं? न्यूरोडाइवर्जेंट व्यक्तियों में अक्सर उल्लेखनीय ताकतें होती हैं। ऑटिस्टिक व्यक्तियों में विस्तार पर असाधारण ध्यान, मजबूत पैटर्न पहचान और विशेष हितों पर गहरा ध्यान हो सकता है। ADHD वाले व्यक्ति अक्सर असाधारण रचनात्मकता, नवीन समस्या-समाधान, और रुचिकर कार्यों पर गहन ध्यान केंद्रित करने की क्षमता प्रदर्शित करते हैं। डिस्लेक्सिक व्यक्ति स्थानिक तर्क और समग्र सोच में उत्कृष्ट हो सकते हैं। इन विशिष्ट क्षमताओं को अपनाने से एक समृद्ध, अधिक विविध दुनिया का निर्माण होता है। हमारे न्यूरोडाइवर्जेंस टेस्ट लेकर अपनी अनूठी प्रोफाइल खोजें।